Thai Language
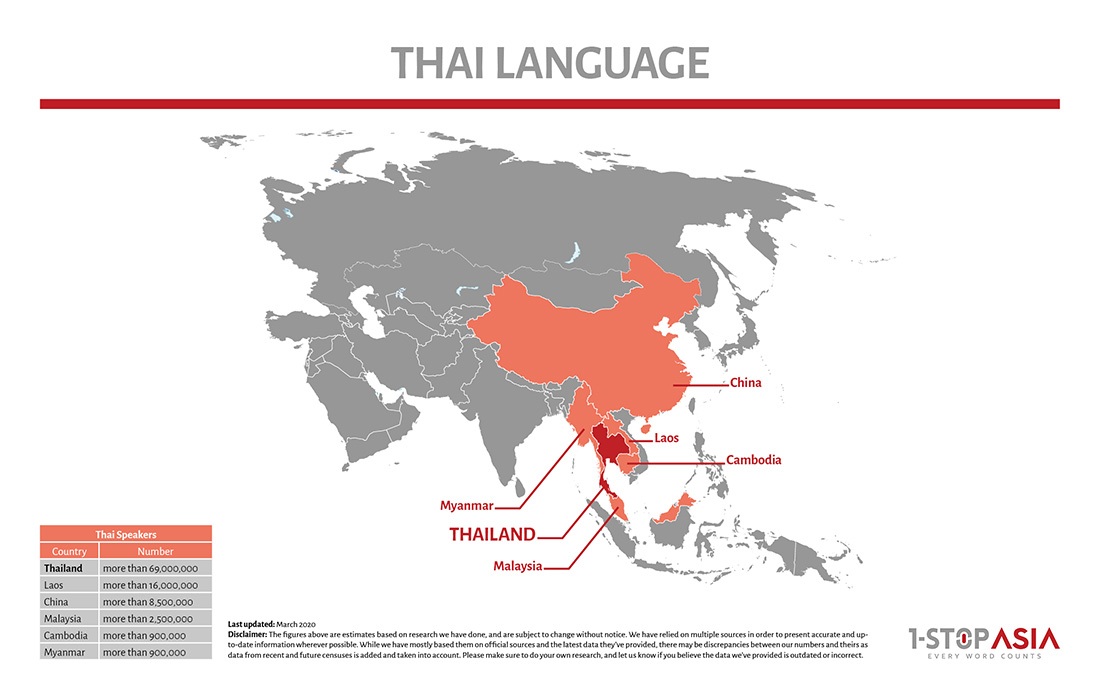
66M Thai Speakers
There are at least five different levels of style and address in Thai languages, depending on whether you are talking to friends, general audience or the royal family.
If you feel it is time to improve your time-management and pay more attention to your clients
The complexity of Thai translation
1. The written language > Translation Service
- Thai translation and localization is as complex as it looks because of the language entailing a deep culture and history, the linguists need to have both the cultural knowledge and the language expertise in order to produce quality translations.
- The culture: Thai culture can be seen through the language they use, which is full of double-meanings, subtle requests, indirect disagreements and more. There are also words that don’t have a direct translation in English. What’s more, they always finish their sentences with a ‘polite particle’ i.e -ka for women speakers and -krab for men. Thus in order to translate the language well, one must have a full understanding of the local culture.
- The respect: Thai people have different ways of addressing people in the conversation and there are multiple layers of complexity when choosing words; from friends, family, the elderly, teachers, bosses, etc. When speaking to monks and royal family, they use a completely different set of vocabulary. Seniority is crucial and it must be adequately conveyed in both written and spoken language.
- The complex vowels. Thai has 6 diphthongs (gliding vowels). They’re a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable, for example, ชั้น, ซึ่ง, เกี่ยว, หมี่.
2. The spoken language > Media Service
When it comes to Thai translation and localization of the spoken language, the diversity of the language is even more evident. Which makes the translation task even more complicated.
- The dialects and accents: There are 4 distinct Thai accents; namely standard/neutral, Northern, Northeast and Southern Thai. The neutral Thai is the main accent spoken by most Thais, while the rest vary according to the geographical location of the user. Each accent has a different speed, and many words differ between them. For instance, the phrase ‘It’s ok’ can have a few versions, some of which are listed below:Standard Thai = ไม่เป็นไร
Southern dialect = ไม่พรือ
Northeastern dialect = บ่เป็นหยัง
Northern dialect = บ่อเป็นหยังเจ้า - The tone: There are 5 tones in Thai, and getting the tone right is important not just because of the accent, but because the meaning can change as the tone does. For example; suay (สวย) means beautiful while zuay (ซวย) means having bad luck or being in an unfortunate situation.
Get exclusive insights into the world of translation, localization, and the language industry.
Our solution for you
Native translators with local knowledge
Our Thai linguists grew up with the language and culture, and our team of experienced translators has been mastering their craft and producing high-quality work for years. Their knowledge of the local culture makes the difference because they can conveyed the content accurately and with as much cultural relevance as possible.
25 years of experience
For over 2 decades in the industry, we’ve cultivated a team of Project Managers who have an in-depth understanding of the industry. And most importantly they, have access to a robust and agile project management system. They’re always there to handle your inquiries, save you time, and deliver great quality translations within the allotted time for each assignment.